Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we perceive and manage data and transactions. As this technology continues to evolve, it becomes increasingly vital to understand its security mechanisms. In this piece, we will deeply explore the basics of blockchain security, examining its core principles, challenges, and best practices . Blockchain security is a critical aspect of the technology’s adoption and success. By implementing robust security measures, we can ensure the integrity and reliability of blockchain networks. As the technology evolves, it is essential to remain vigilant and stay ahead of potential threats.
Introduction to Blockchain Technology

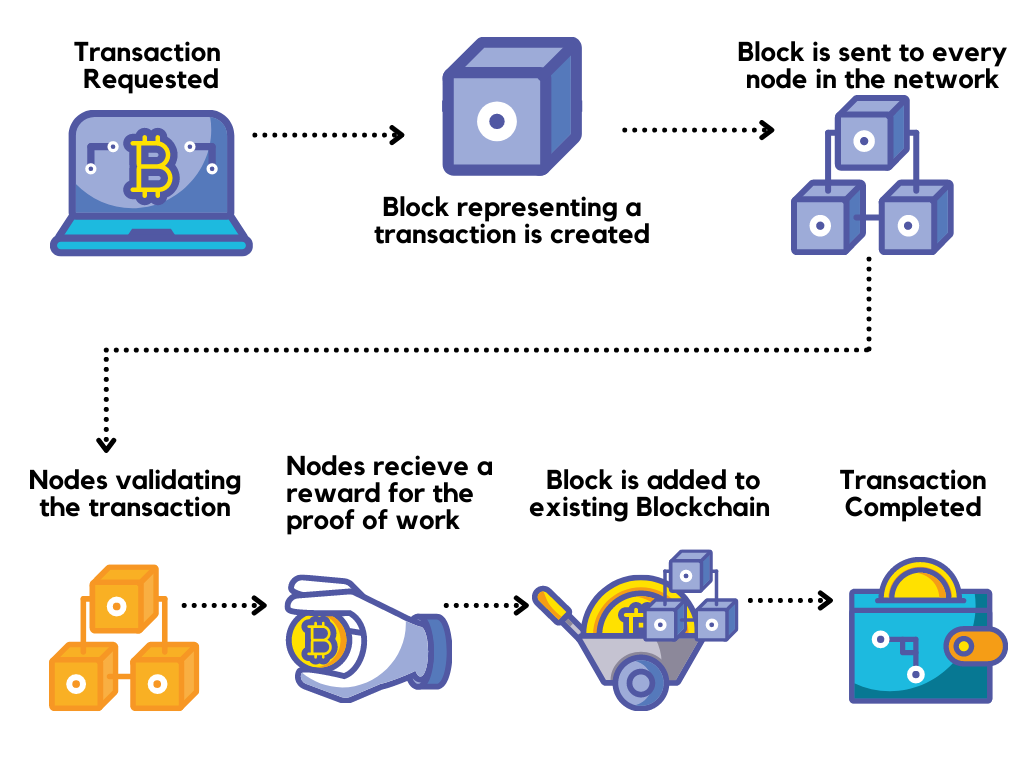
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that operates on a decentralized network of computers. It allows the secure and transparent recording of transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks or financial institutions. Each transaction, known as a block, is cryptographically linked to the previous one, forming a chain.
How Does Blockchain Work?
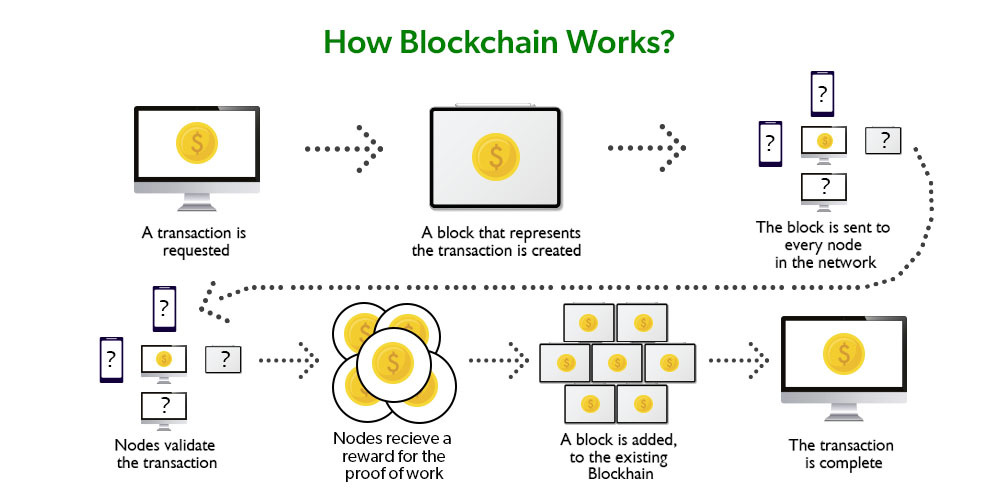
In a blockchain network, each participant maintains a copy of the entire ledger, eliminating the single point of failure. Transactions are added to the chain through a consensus mechanism, ensuring that all participants agree on the validity of new blocks.
Key Components of a Blockchain
![The main components of Blockchain [32]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335163861/figure/fig2/AS:791783554424837@1565787318355/The-main-components-of-Blockchain-32.png)
A blockchain comprises several essential components, including nodes, blocks, transactions, and consensus algorithms. Nodes are the individual computers that participate in the network, while blocks store batches of transactions.
Decentralization and Consensus Mechanism
Blockchain’s decentralized nature makes it highly secure as there is no central point vulnerable to attacks. Additionally, the consensus mechanism ensures that the majority of participants validate transactions, reducing the risk of fraudulent activities.
Cryptography and Hashing
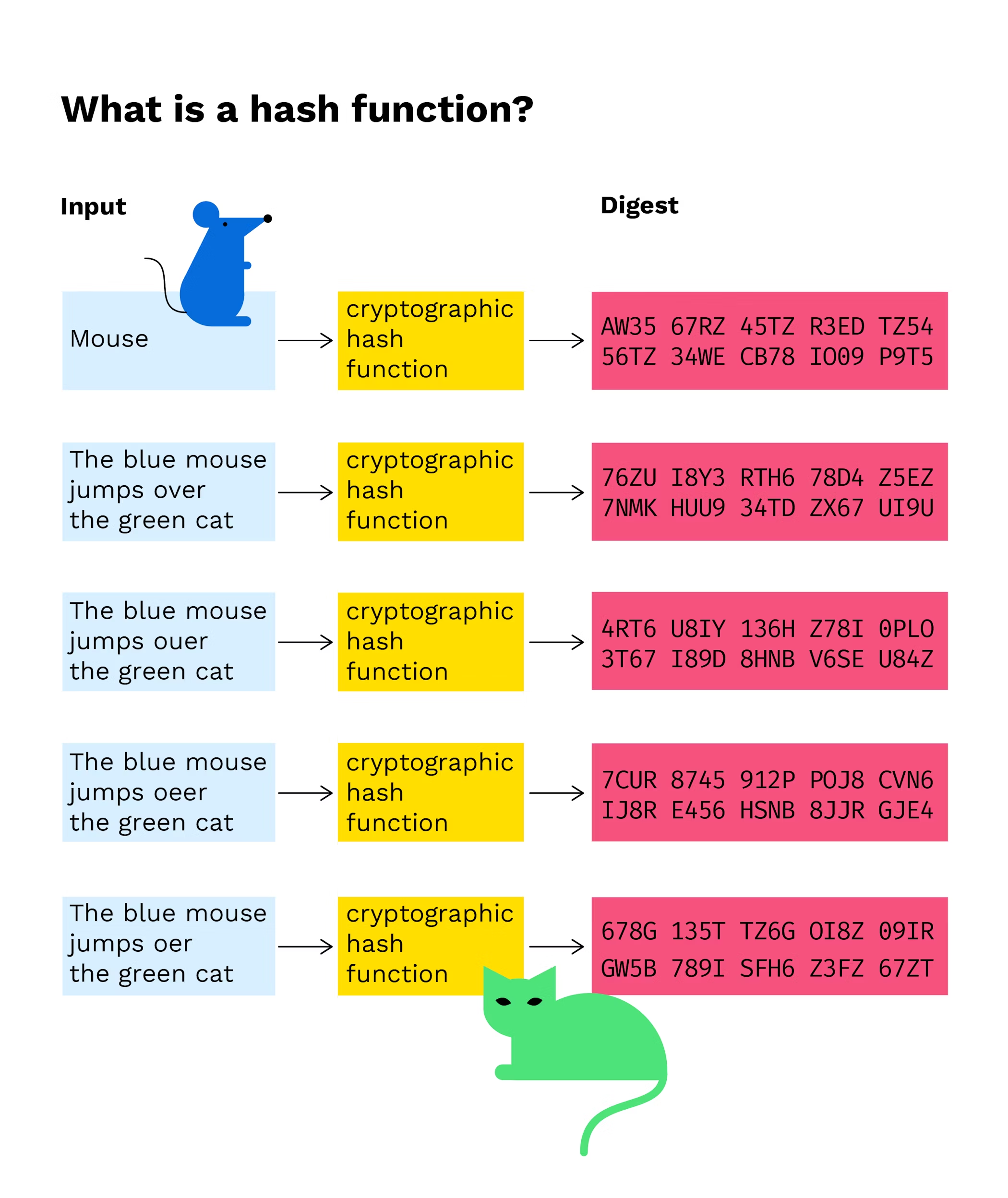
Blockchain employs sophisticated cryptographic methods to ensure the security of transactions and uphold the integrity of data. Hashing algorithms convert data into fixed-length strings, making it challenging for attackers to tamper with information.
Immutability and Tamper Resistance
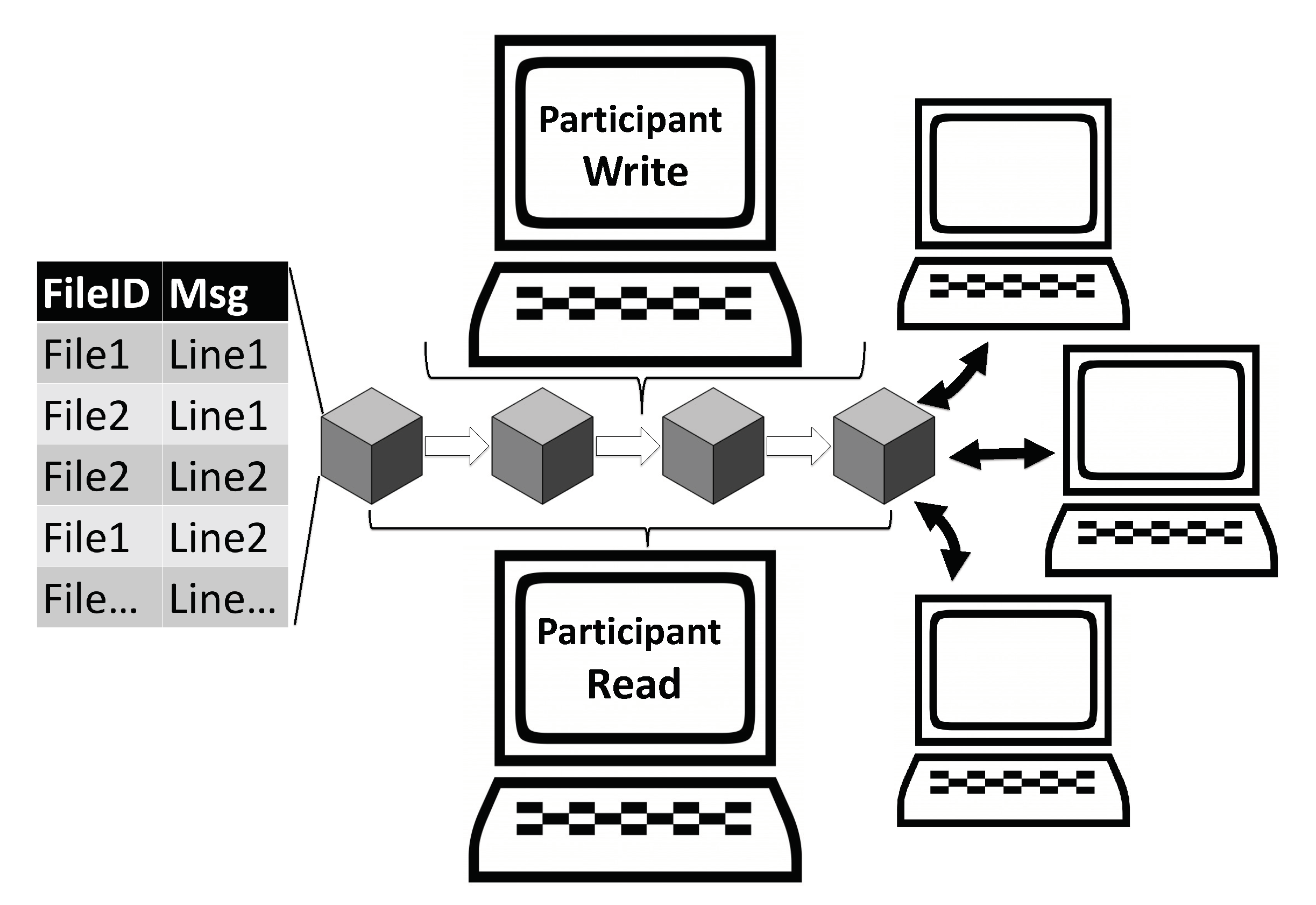
Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes immutable, meaning that altering its content is practically impossible. This tamper resistance enhances the security and trustworthiness of the network.
51% Attack
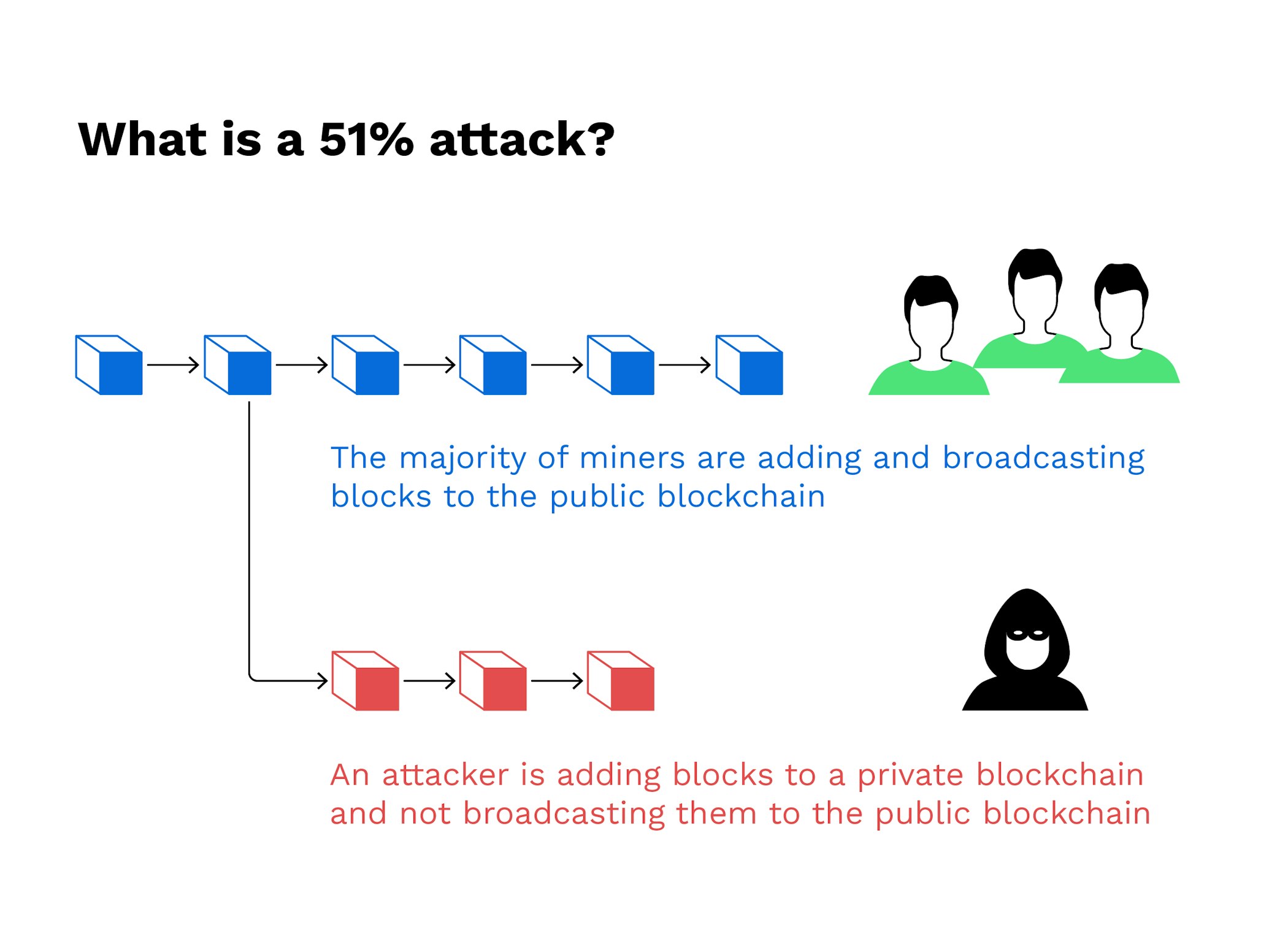
A 51% attack occurs when an entity gains control over the majority of the network’s computing power. This dominance enables the attacker to manipulate transactions and potentially double-spend digital assets.
Double Spending
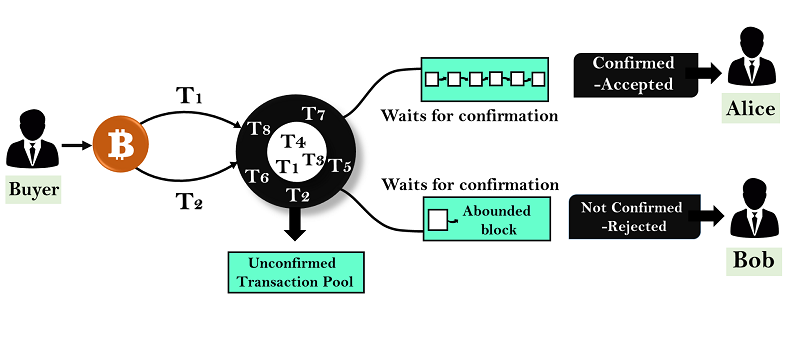
Double spending involves spending the same digital asset more than once, leading to a loss of value and trust in the blockchain network.
Smart Contract Bugs
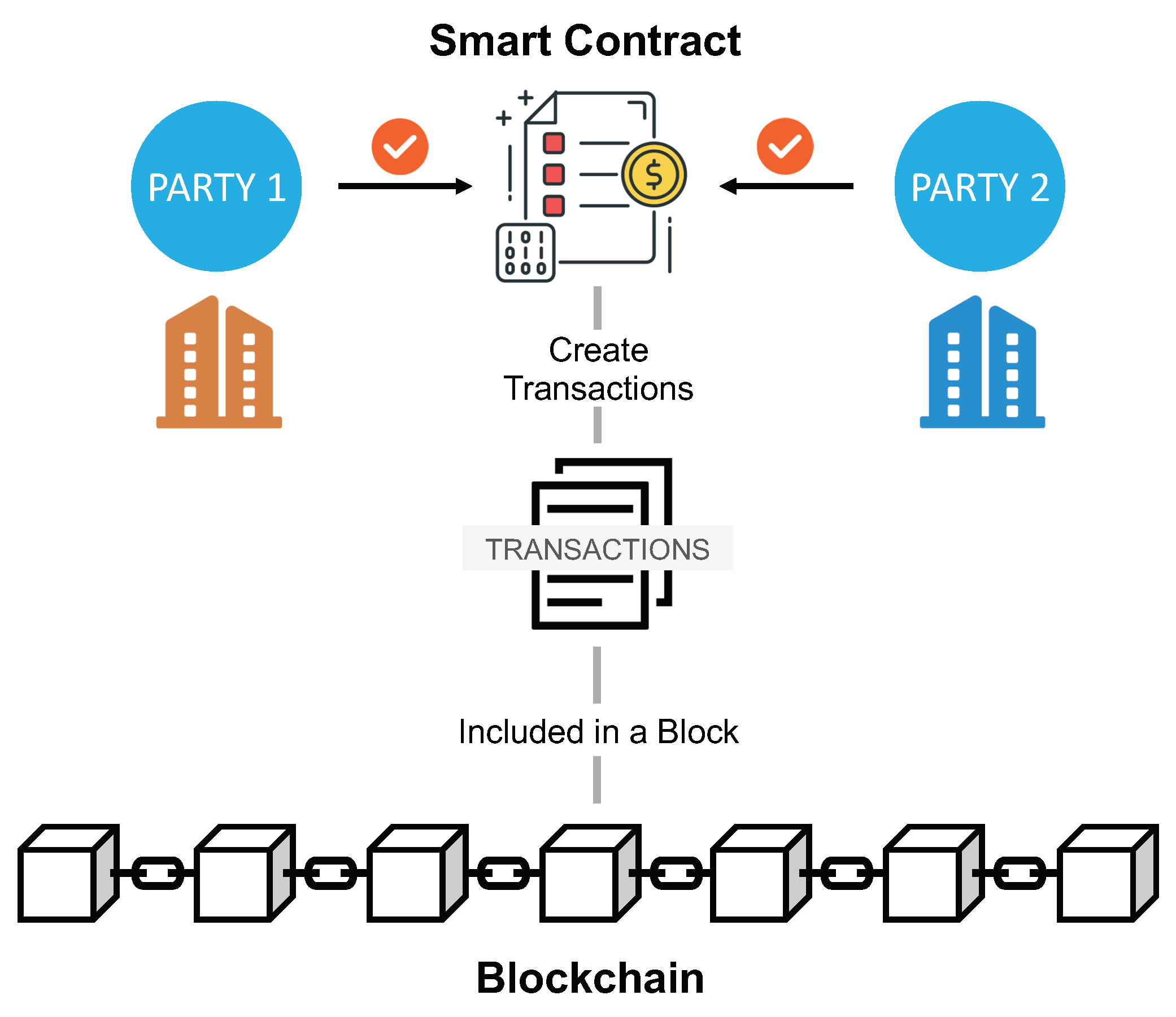
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with predefined conditions. Vulnerabilities in smart contracts can lead to exploits, resulting in financial losses.
Public and Private Key Management
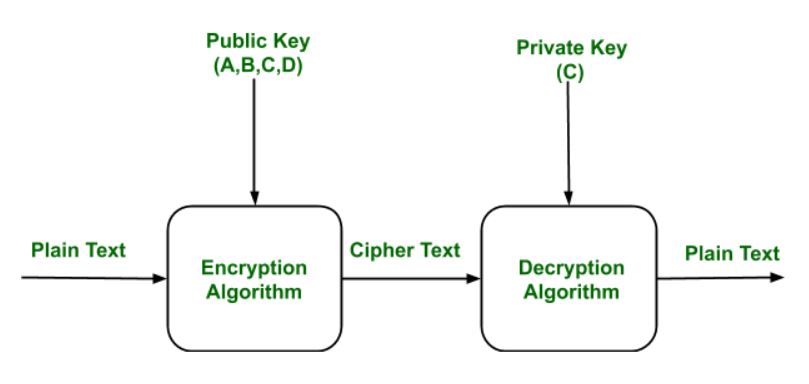
Public and private keys are used to sign and verify transactions on the blockchain. Proper key management is crucial to prevent unauthorized access to digital assets.
Multi-factor Authentication
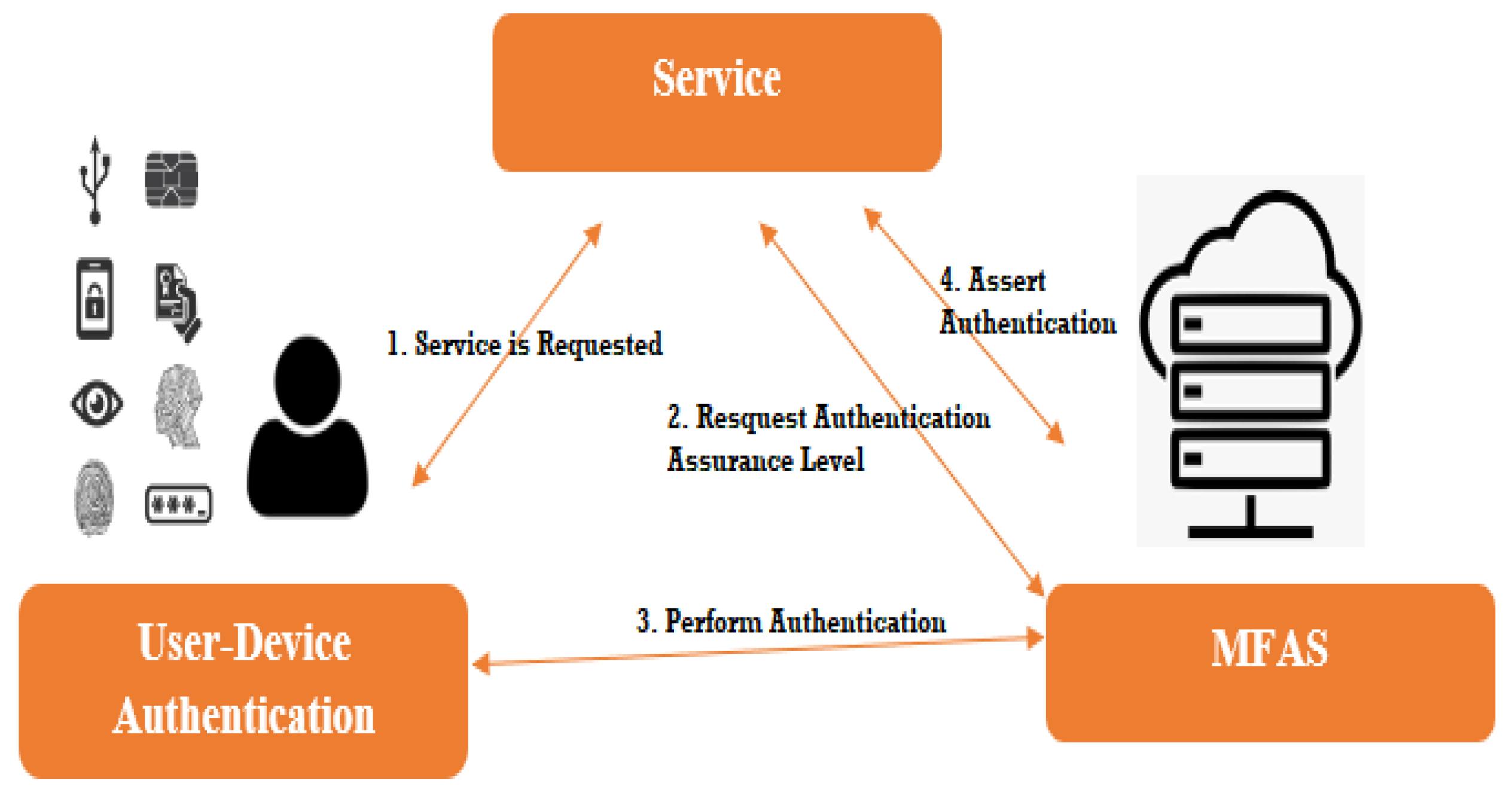
Implementing multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Regular Software Updates

Frequent software updates help patch vulnerabilities and ensure the latest security features are in place.
Blockchain and Data Privacy

Blockchain transactions are pseudonymous, as they are linked to unique addresses rather than personal information. However, complete anonymity can be challenging to achieve.
GDPR Compliance

Blockchain projects handling personal data must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to protect user privacy.
User Control over Personal Data
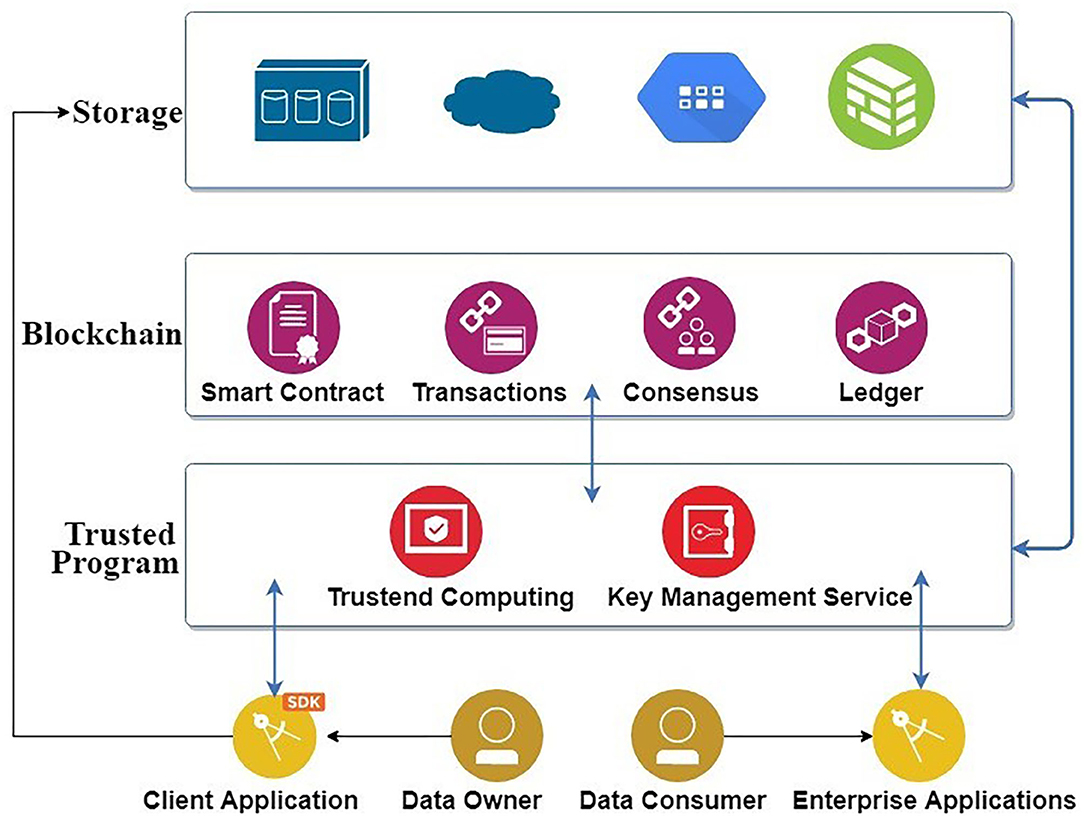
Some blockchain projects allow users to have full control over their personal data and choose who can access it.
Interoperability and Scalability Challenges
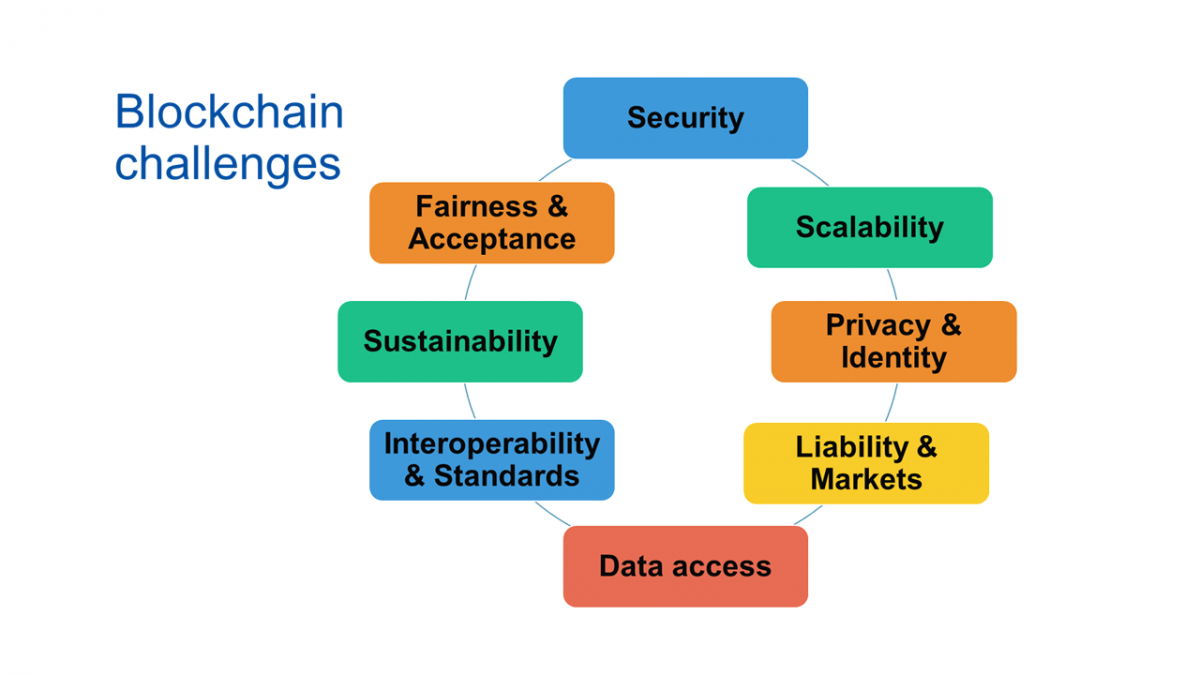
Interoperability enables different blockchains to communicate and share data, but challenges remain in achieving seamless cross-chain interactions.
Solutions for Scalability Issues

Scalability is a major concern in blockchain, as increased usage can slow down the network. Various solutions are being explored to address this challenge.
The Role of Interoperability in Security

Interoperability can enhance security by enabling the exchange of critical information between different blockchains.
KYC and AML Compliance
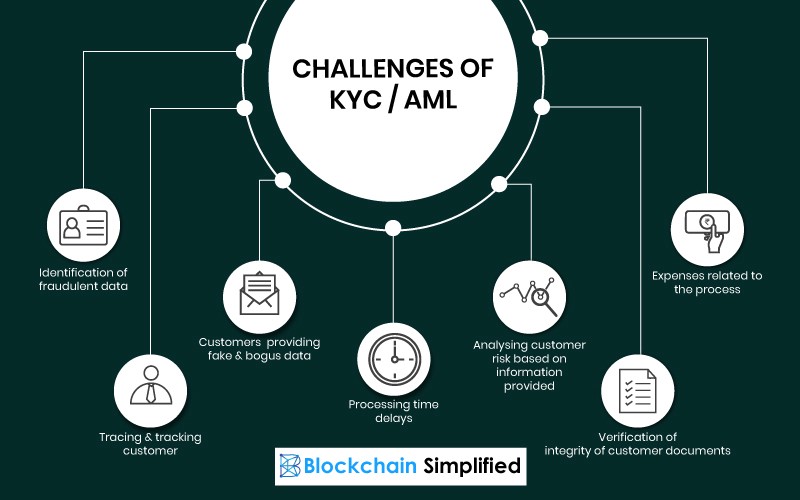
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations apply to blockchain-based projects involving financial transactions.
Legal Recognition of Smart Contracts
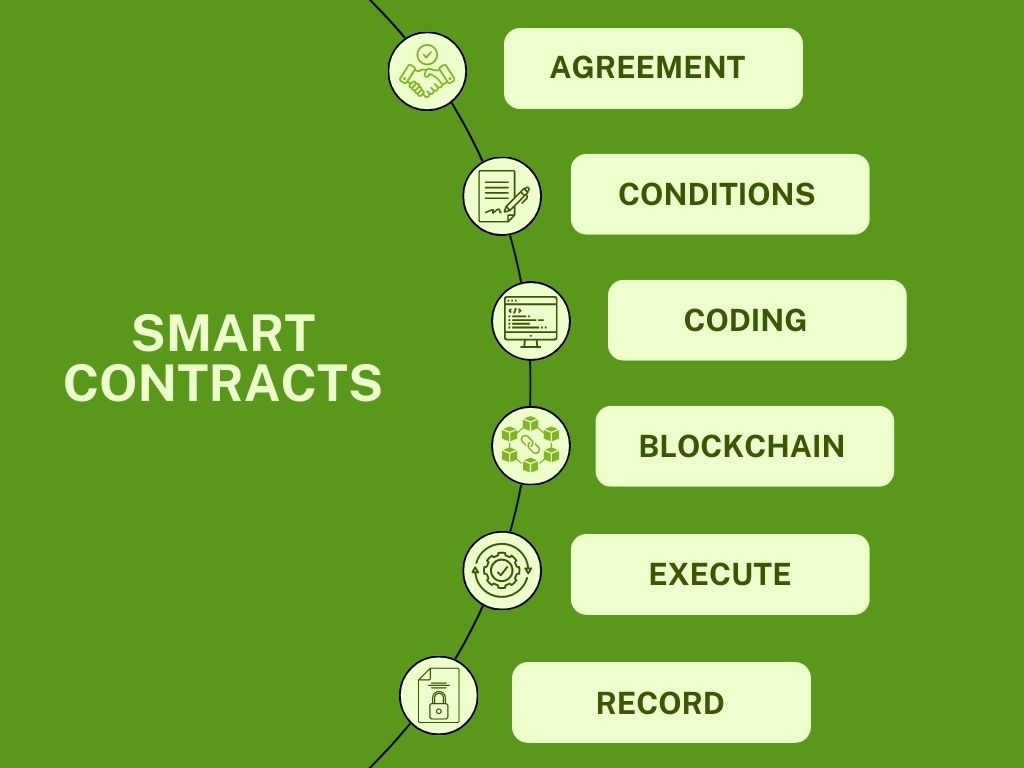
The legal recognition of smart contracts is an evolving area, with some jurisdictions accepting them as legally binding agreements.
Government Oversight and Blockchain

Regulators are actively monitoring blockchain developments to ensure compliance with existing laws and regulations.
Importance of Regular Audits

Regular security audits are vital to identify vulnerabilities and enhance the overall security of blockchain networks.
Third-Party Auditing Firms
Third-party auditing firms provide unbiased assessments of blockchain projects’ security posture.
Addressing Discovered Vulnerabilities
Once vulnerabilities are identified, prompt action should be taken to fix them and prevent potential exploits.
Quantum Resistance

With the rise of quantum computing, there is a need to develop quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms to protect blockchain networks.
Decentralized Identity Management

Decentralized identity management solutions aim to give individuals more control over their digital identities and personal data.
Artificial Intelligence in Blockchain Security

Artificial intelligence can be utilized to detect and respond to security threats more effectively.
Summary
Blockchain security is paramount to the continued growth and adoption of this transformative technology. By understanding the principles of blockchain security and implementing best practices, we can safeguard blockchain networks from potential threats and ensure a more secure digital future.
FAQs
What makes blockchain secure?
Blockchain’s security stems from its decentralized nature, cryptographic techniques, and immutability.
What are the common vulnerabilities in blockchain?
Common vulnerabilities include 51% attacks, double spending, and smart contract bugs.
How can blockchain projects comply with data privacy regulations?
Blockchain projects must adopt pseudonymity, adhere to GDPR guidelines, and allow user control over personal data.
How can blockchain achieve scalability?
Blockchain can achieve scalability through solutions like sharding, layer 2 protocols, and optimized consensus algorithms.
Why is quantum resistance crucial for blockchain?
Quantum-resistant algorithms protect blockchain networks from potential attacks by quantum computers.
